1. Factors Affecting Capsule Dissolution in the Body
2. Typical Dissolution Time of Gelatin Capsules
3. Scientific Studies and Standards
4. Common Questions Answered
5. Practical Considerations for Patients and Manufacturers
6. Summary
Under normal gastric conditions, most gelatin capsules dissolve within 10 to 30 minutes. Ideally, under fasting conditions, the dissolution time may be as long as 5 to 15 minutes. However, the capsule 's formulation and in vivo conditions can affect the dissolution time of a gelatin capsule .
Factors Affecting Capsule Dissolution in the Body

Capsule Formulation Factors

1.Capsule Composition and Thickness
Gelatin is the main material used for capsule shells. If the capsule wall is thick or contains additives (like titanium dioxide or colorants), the shell takes longer to soften and break apart. A thin-walled capsule may dissolve in as little as 10–12 minutes , while a thicker or specially coated capsule might need 20–30 minutes or more.
2. Size of the Capsule
With larger capsules, water has to travel a longer distance from the outside of the capsule shell to the drug in the core, resulting in a longer overall dissolution time. A small size 4 capsule might disintegrate in about 10 minutes , while a large size 00 capsule might take closer to 20 minutes .
3. Fill Material (Excipients and Drug Formulation)
The contents of the capsule can also affect its dissolution time . Powders that absorb water quickly help the capsule shell break down faster, accelerating dissolution. On the other hand, oily or waxy fillers don't mix with gastric fluids and can slow the capsule 's disintegration. In these cases, the dissolution time may exceed 30 minutes .
4. Special Coatings (Enteric Capsules)
Enteric-coated capsules are specially treated to prevent them from dissolving in the stomach. Enteric-coated gelatin capsules can withstand acidic pH and remain intact for more than 2 hours until they reach the small intestine, where they dissolve in the higher pH environment.
Physiological conditions in the body
1. Stomach pH and Acidity
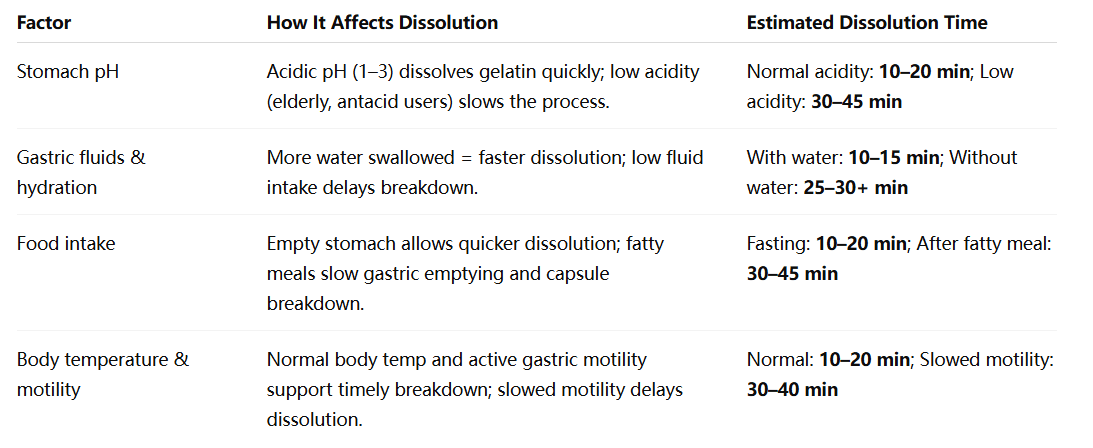
The acidic environment of the stomach (pH 1-3 under fasting conditions) generally helps gelatin dissolve quickly. However, dissolution may be slowed in people with reduced stomach acid (for example, the elderly or those taking antacids). In a low-acid environment, the capsule may remain intact for 30-45 minutes instead of dissolving quickly.
2. Gastric Fluids and Hydration
Gelatin requires water to dissolve. If you take the capsule with water, the capsule shell will absorb the water faster and break down faster.
3. Food Intake
Whether or not food has been consumed significantly affects the dissolution rate of the capsule. In the fasting state, the capsule typically dissolves within the expected 10-20 minutes . After a large meal, gastric emptying is slower, and gastric contents may coat the capsule, extending the dissolution time to 30-45 minutes . High-fat meals, in particular, can delay capsule dissolution.
4. Body Temperature and Gastric Motility
dissolves faster at higher temperatures , so a normal body temperature of 37°C supports the breakdown of gelatin .
Typical Dissolution Time of Gelatin Capsules
In standard laboratory testing (37°C in simulated gastric fluid), most uncoated
hard gelatin capsules dissolve within 10 to 20 minutes . In the real-life human stomach, where conditions vary, a typical range is 10 to 30 minutes . Soft gelatin capsules, with their thinner shells and liquid fills, typically dissolve faster , sometimes within 10-15 minutes .
However, dissolving the capsule shell is only the first step. After the shell dissolves, the drug or supplement must still dissolve into solution and then be absorbed through the intestinal wall to be effective. This is why manufacturers simulate testing for disintegration time (the breakdown of the capsule shell) and dissolution time (the release of the drug into solution).
Scientific Studies and Standards
Pharmaceutical testing is guided by official standards. The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) <2040> specifies that most dietary supplement capsules should disintegrate within 30 minutes under test conditions. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also requires dissolution testing to ensure consistent bioavailability for medicines.
Scientific research confirms that dissolution rate is largely dependent on gastric acidity and capsule design. For example, a study published in PubMed indicates that gelatin capsules dissolve more rapidly in acidic conditions but dissolve much more slowly at pH values above 5. This explains why patients taking acid-lowering medications, such as proton pump inhibitors, sometimes experience delayed capsule dissolution.
Common Questions Answered
Do gelatin capsules dissolve in water before ingestion?
Yes, gelatin is water-soluble. If you place the capsule in water, it will eventually dissolve . However, at room temperature, this process may take several hours. In a warm, acidic stomach, the dissolution process is much faster.
Do vegetarian capsules dissolve faster or slower than gelatin?
Vegetarian capsules , unlike gelatin capsules, are typically made of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) . Gelatin capsules dissolve and disperse rapidly upon contact with water (or stomach acid). HPMC capsules, on the other hand , first absorb water and swell, forming a gel-like outer layer. This gel layer then gradually breaks down, releasing the contents. Throughout the experiment, vegetarian capsules dissolve more slowly, taking more steps . However, in the stomach, gastric peristalsis accelerates the breakdown of the gel layer, resulting in similar dissolution rates for both, taking 10-30 minutes.
What happens if a capsule doesn't dissolve properly?
If a capsule passes through the stomach without dissolving fully, the active ingredient may not be absorbed properly, reducing the product's effectiveness. This is why dissolution testing is a critical step in manufacturing .
Why do some supplements add coatings to capsules?
Coatings are added to mask taste, control release time, or protect sensitive ingredients from stomach acid. For example, probiotics are often administered in enteric-coated capsules to ensure they reach the intestine alive.
How do storage conditions affect dissolution?
Capsules stored in humid or hot conditions may become sticky or brittle. Proper storage in a cool, dry place ensures that the capsules maintain their designed dissolution profile.
Practical Considerations for Patients and Manufacturers
The most practical advice for patients is to take the capsule with plenty of water, avoid lying down immediately after swallowing, and follow the instructions for taking it with or without food. These actions will ensure that the capsule dissolves on time and the active ingredients are effectively absorbed.
For manufacturers, dissolution testing is a critical part of quality control. During product development, capsules need to be tested under simulated gastric and intestinal conditions to ensure they break down at the correct time. Regulators require these tests before a new drug or supplement can be marketed.
Summary
In most cases, gelatin capsules dissolve in the stomach over a period of 10 to 30 minutes , releasing their contents for absorption. The exact time depends on factors such as capsule size and thickness, formulation, stomach acidity, amount of water consumed, and whether the patient has recently eaten. Hard gelatin capsules generally take longer to dissolve than soft gelatin capsules, while coated capsules may delay release in the intestine. Both patients and manufacturers need to understand these variables, as reliable dissolution is crucial to drug effectiveness.
At LTPM CHINA , we specialize in high-quality capsule filling machines and turnkey pharmaceutical solutions. Whether you are producing hard gelatin capsules or softgels, our equipment is designed to maintain consistency, accuracy, and compliance with international dissolution standards. Contact us today to learn how we can support your capsule production line with customized machinery and expert guidance .
